Featured Creatures: Varroa destructor Anderson and Trueman (Arachnida: Acari: Varroidae)
July 28, 2014
From: University of Florida
common name: varroa mite
scientific name: Varroa destructor Anderson and Trueman (Arachnida: Acari: Varroidae)
Introduction – Distribution – Description – Life Cycle – Economic Importance – Detection – Management – Selected References
Introduction (Back to Top)
The varroa mite, Varroa destructor Anderson and Truemann, is the world’s most devastating pest of Western honey bees, Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Although the varroa complex includes multiple species, V. destructor is the species responsible for the vast majority of the damage attributed to mites from this genus. Until 2000, it was believed that V. jacobsoni Oudemans was the mite responsible for widespread honey bee colony losses. However, taxonomic work published in 2000 (Anderson and Trueman 2000) indicated that a previously-unidentified species of varroa (V. destructor) was responsible for the damage, while V. jacobsoni was shown to be only moderately harmful to western honey bees. This publication is limited to V. destructor.
Varroa mites are ectoparasites that feed on the hemolymph of immature and adult honey bees. Apis mellifera, the Western honey bee, is not the mite’s natural host. In fact, the mite is native to Asia where it parasitizes another cavity-dwelling honey bee, A. cerana (the eastern or Asian honey bee). Apis cerana is believed to have some natural defenses against the mite and consequently rarely is affected negatively by the mite. Only when colonies of A. mellifera were brought to Asia did people begin to realize how devastating the mites could be. Varroa’s host shift did not occur instantly, as evidence suggests that it may have taken 50-100 years (Webster and Delaplane 2001). Since that time, the mite has spread around the world and has become nearly-cosmopolitan in distribution. Those countries not hosting varroa mites maintain strict quarantine procedures to lessen the chance of an accidental importation of the mite.
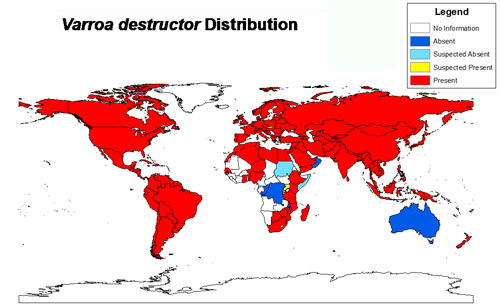
Distribution (Back to Top)
Figure 1. Current varroa mite distribution – 2010. Red areas indicate establishment of Varroa destructor.
Leave a Comment